This method calculates the depreciation cost without considering the salvage value. The depreciation rate is used to calculate an asset’s annual depreciation, and then all accumulated depreciation from the first year of use until the last year of usage is added. The straight-line method of depreciation isn’t the only way businesses can calculate the value of their depreciable assets. While the straight-line method is the easiest, sometimes companies may need a more accurate method. This means taking the asset’s worth (the salvage value subtracted from the purchase price) and dividing it by its useful life.
Understanding the Straight-Line Method

While you now have a solid foundation, the details of depreciation and how it affects taxes and financial statements can be important considerations. Embracing technology in your depreciation calculations can lead to more accurate financial reporting, improved efficiency, and better decision-making. By choosing the right tools and implementing them effectively, you can transform what was once a tedious task into a streamlined process that adds value to your business.
Best Online Bookkeeping Services of 2024
Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. In closing, the net PP&E balance for each period is shown below in the finished model output. Once repeated for all five years, the “Total Depreciation” line item sums up the depreciation amount for the current year and all previous periods to date. Here, we are assuming the Capex outflow is right at the beginning of the period (BOP) – and thus, the 2021 depreciation is $300k in Capex divided by the 5-year useful life assumption. In a full depreciation schedule, the depreciation for old PP&E and new PP&E would need to be separated and added together. Note that for purposes of simplicity, we are only projecting the incremental new capex.
How do accountants calculate depreciation?
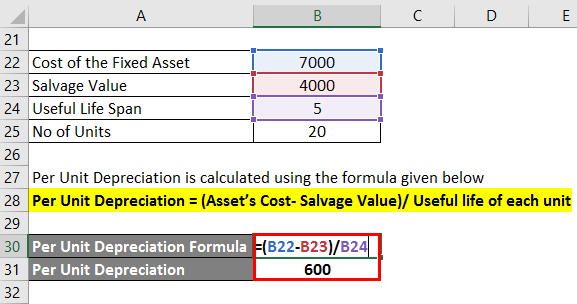
- Here useful life in the form of unit produced is the total unit produced in the year divided by total expected units to be produced.
- Because large losses are realized early, the tax benefit will be spread over a longer period.
- For assets purchased in the middle of the year, the annual depreciation expense is divided by the number of months in that year since the purchase.
- This approach can provide a more accurate representation of an asset’s value over time for certain types of equipment or machinery.
- Thus, the cash flow statement (CFS) or footnotes section are recommended financial filings to obtain the precise value of a company’s depreciation expense.
The difference between the end-of-year PP&E and the end-of-year accumulated depreciation is $2.4 million, which is the total book value of those assets. To start, a company must know an asset’s cost, useful life, and salvage value. Then, it can calculate depreciation using a method suited to its accounting needs, asset type, asset lifespan, or the number of units produced. Depreciation is an accounting method that companies use to apportion the cost of capital investments with long lives, such as real estate and machinery. The sum-of-the-years’-digits method (SYD) accelerates depreciation as well but less aggressively than the declining balance method.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Conceptually, the depreciation expense in accounting refers to the gradual reduction in the recorded value of a fixed asset on the balance sheet from “wear and tear” with time. The depreciation expense reduces the carrying value of a fixed asset (PP&E) recorded on a company’s balance sheet based on its useful life and salvage value assumption. This amount will be depreciated over its useful life using an appropriate depreciation method (e.g., straight-line, declining balance, etc.). If your company uses a piece of equipment, you should see more depreciation when you use the machinery to produce more units of a commodity.
What is your current financial priority?
Depreciation measures the value an asset loses over time—directly from ongoing use (through wear and tear) and indirectly from the introduction of new product models (plus factors such as inflation). Writing off only a portion of the cost each year, rather than all at once, also allows businesses to report higher net income in the year of purchase than they would otherwise. Carrying value is the net of the asset xero partner programme account and the accumulated depreciation. Salvage value is the carrying value that remains on the balance sheet after which all depreciation is accounted for until the asset is disposed of or sold. Salvage value is what a company expects to receive in exchange for the asset at the end of its useful life. The method you choose should align with your business’s specific needs, asset types, and financial goals.
So in this example, the declining balance method would only be advantageous for the first year. To see how the calculations work, let’s use the earlier example of the company that buys equipment for $25,000, sets the salvage value at $2,000 and the useful life at five years. Learn how to calculate your depreciable cost, the depreciable cost formula, and how Enerpize can help you calculate your depreciable.
It may not accurately reflect the depreciation pattern of assets that lose value more quickly in the early years. It doesn’t account for changes in an asset’s productivity or value over time. The straight-line method assumes that an asset loses its value evenly over its useful life. This means the depreciation expense remains constant each year, making it easy to predict and budget for future expenses.
The amount an asset is depreciated in a given period of time is a representation of how much of that asset’s value has been used up. This process ensures compliance with accounting standards and provides a clearer picture of your business’s financial health. Accurate depreciation calculations contribute to more precise financial reporting, which in turn supports informed decision-making. Tracking business expenses, including depreciation, can be made easier with accounting software. This software can be an invaluable tool for managing your company’s financial records. Acquiring assets throughout the fiscal year rather than precisely on January 1st is a common practice for business owners.
Depreciation determined by this method must be expensed in each year of the asset’s estimated lifespan. Let us take another example to understand the unit of production method formula. A company called beta limited just started its business of manufacturing empty biodegradable water bottles.
11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. The concept of useful life represents the period beyond which it would not be practical to use an asset anymore. In this example, we can say that the service given by the weighing machine in its first year of life was $200 ($1,000 – $800) to the company. Depreciation is allocated over the useful life of an asset based on the book value of the asset originally entered in the books of accounts.